What Is a Wellness Exam for Dogs? Importance, Benefits, and What to Expect at the Vet
Understanding What Is a Wellness Exam for Dogs
A wellness exam for dogs assesses overall canine health, even when no symptoms are present. My veterinarian evaluates several health markers and tracks changes over time. This routine visit focuses on prevention and early detection of issues like dental disease, obesity, or parasites.
Key Components Included in a Dog Wellness Exam:
| Component | Standard Actions | Context Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Inspect eyes, ears, skin, coat, oral cavity | Look for lumps, dental tartar, red gums |
| Vaccination Review | Check immunization records, update as required | Annual rabies, distemper boosters |
| Parasite Screening | Test for heartworms, intestinal parasites | Flea checks, fecal analysis |
| Weight Assessment | Monitor weight, assess body condition score | Identify obesity or weight loss |
| Blood Work | Test organ function, detect hidden issues | CBC, chemistry panel |
My veterinarian asks targeted questions about appetite, water consumption, exercise, and behavior. This information builds a complete health history, helping spot subtle changes quickly.
Typical Dog Wellness Exam Schedule by Age:
| Dog Age Group | Frequency of Wellness Exams | Context Terms |
|---|---|---|
| Puppy (Under 1) | Every 3–4 weeks | Core vaccine schedule |
| Adult (1–7) | Annually | Routine prevention |
| Senior (7+) | Every 6 months | Age-related screening |
Regular wellness exams optimize early problem detection and maintain preventive healthcare. When I schedule consistent veterinary checkups based on my dog’s age and medical needs, I help ensure they remain healthier for longer.
Key Components of a Dog Wellness Exam
A comprehensive dog wellness exam covers multiple aspects of canine health. I focus on evaluations and screenings that support early detection and preventive care for dogs at every life stage.
Physical Health Assessment
I perform a physical health assessment by examining visible body systems. I observe the skin, coat, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, limbs, and abdomen for abnormalities. I listen to the heart and lungs for irregularities and check vital signs. Palpation of the joints and lymph nodes helps me detect pain, swelling, or growths.
| Body System | Assessment Method | Key Observations |
|---|---|---|
| Skin & Coat | Visual/Manual | Parasites, lesions, hair loss |
| Eyes & Ears | Visual | Redness, discharge, cloudiness |
| Mouth & Teeth | Visual/Palpation | Dental calculus, gum disease |
| Limbs & Joints | Palpation | Swelling, pain, range of motion |
| Heart & Lungs | Stethoscope | Murmurs, arrhythmias, breathing |
Vaccinations and Preventive Care

I review vaccination records and recommend core or non-core vaccines based on the dog’s health status and environment. I update necessary vaccinations and discuss parasite prevention, including flea, tick, and heartworm products. If the dog lives in a high-risk area, I adjust the vaccination or prevention plan accordingly.
| Core Vaccine | Booster Frequency | Prevented Disease |
|---|---|---|
| Rabies | 1-3 years | Rabies virus |
| Distemper | 1-3 years | Canine distemper virus |
| Parvovirus | 1-3 years | Canine parvovirus |
| Adenovirus | 1-3 years | Canine hepatitis |
Dental and Oral Health Check
I examine teeth and gums for signs of tartar, gingivitis, tooth fractures, or oral tumors. Bad breath, excessive drooling, or reluctance to eat may prompt further x-rays or dental cleaning.
| Dental Indicator | Possible Issue |
|---|---|
| Gum redness | Gingivitis |
| Tartar accumulation | Periodontal disease |
| Broken/missing tooth | Dental trauma/infection |
| Foreign body | Oral injury |
Nutritional Evaluation
I assess diet quality, feeding frequency, and portion sizes. I monitor body condition score and muscle tone to detect overfeeding or malnutrition. If allergies, chronic conditions, or obesity exist, I tailor dietary recommendations.
| Assessment Area | Evaluation Metric | Adjustment Example |
|---|---|---|
| Body condition | 1–9 BCS scale | Adjust food volume |
| Weight change | % increase/decrease | Modify caloric intake |
| Muscle tone | Visual inspection | Recommend protein adjustment |
| Coat quality | Sheen/texture | Suggest fatty acid supplementation |
Why Wellness Exams Are Important for Dogs
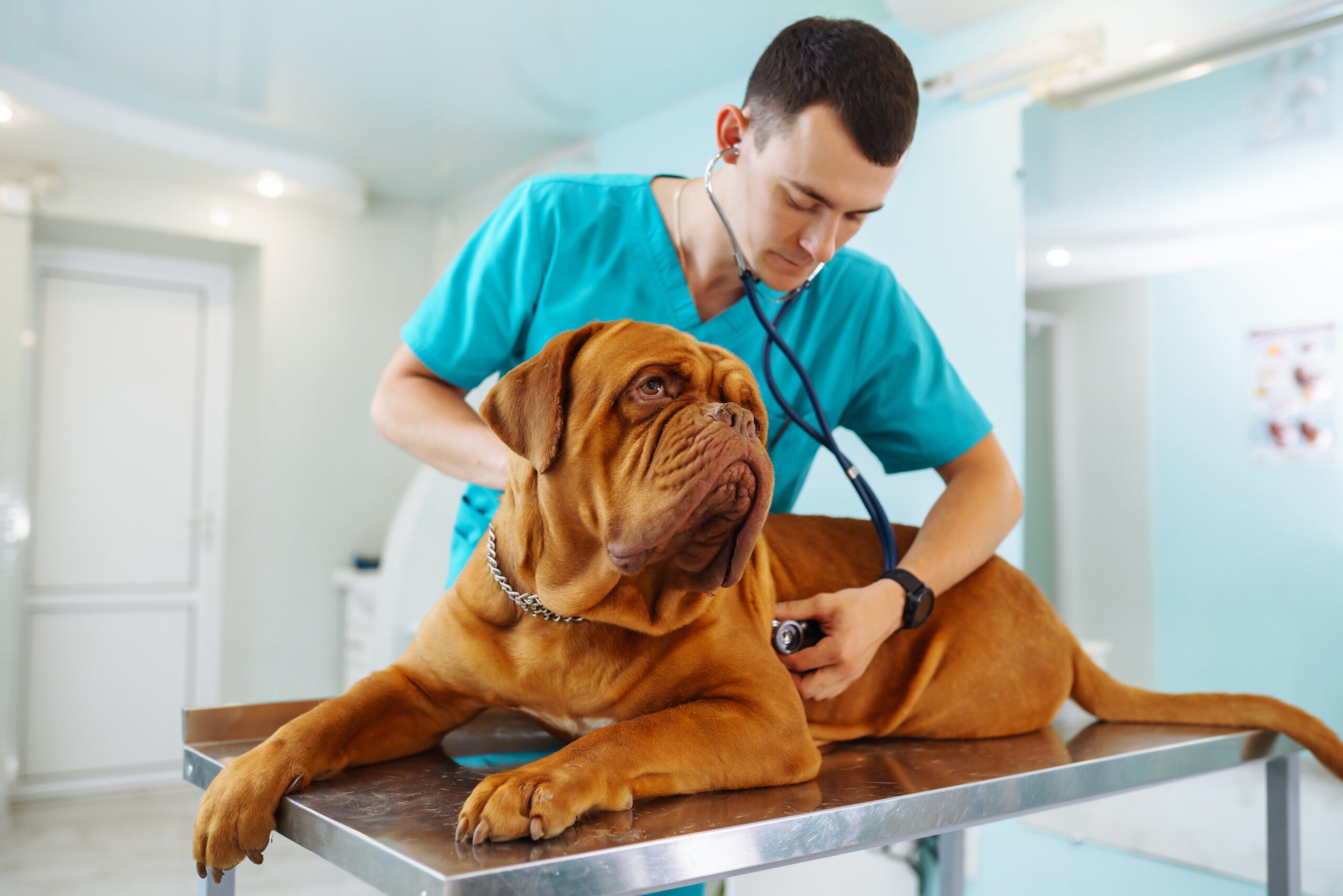

Regular wellness exams for dogs optimize early detection of diseases and conditions, even when symptoms aren’t obvious. Detecting health changes promptly supports more effective treatment, preventing minor problems from escalating into serious ones. Proactive monitoring extends a dog’s healthy lifespan and helps avoid advanced illnesses.
Wellness exams include reviews of vaccination status, parasite control, and routine screenings. These actions reduce transmission risks for diseases like rabies, distemper, and heartworm. Annual or biannual checkups enable targeted prevention strategies based on each dog’s age and lifestyle.
Wellness evaluations foster stronger relationships between dogs, owners, and veterinarians. Routine communication about a dog’s habits or new behaviors makes it easier for me to catch subtle health shifts early. Early intervention lowers overall long-term veterinary costs, reducing expenses tied to late-stage treatments.
Common Benefits of Wellness Exams
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Early Disease Detection | Identifies issues such as heart disease, kidney problems, and tumors before symptoms show |
| Vaccination and Parasite Prevention | Ensures current protection against infectious diseases, ticks, fleas, and intestinal worms |
| Nutritional and Weight Guidance | Adjusts feeding plans based on life stage and body condition |
| Dental Health Monitoring | Detects tartar, gum disease, or oral pain early |
| Baseline Health Data | Tracks vital signs and any health changes over time |
Skipping routine exams raises health risks for adult and senior dogs. Missed screenings delay diagnosis, leading to shorter, less comfortable lives. Maintaining scheduled exams offers a foundation for preventive care and a longer, happier life for my dog.
Age-Based Frequency of Wellness Exams
| Life Stage | Frequency | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Puppy | Every 3–4 weeks | Initial vaccines, growth tracking |
| Adult | Annually | Annual physical, vaccine boosters |
| Senior | Every 6 months | Biannual screenings, age-related disease checks |
How Often Should Dogs Have Wellness Exams?
Dog wellness exam frequency depends on age, health status, and individual risk factors. Puppies, adult dogs, and seniors have distinct needs that shape their optimal exam schedules.
Recommended Dog Wellness Exam Frequency by Life Stage
| Life Stage | Age Range | Wellness Exam Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Puppy | 0–12 months | Every 3–4 weeks |
| Adult | 1–6 years | Annually |
| Senior | 7+ years | Every 6 months |
Puppies get examined every 3–4 weeks until about 16 weeks old, since rapid growth and developing immunity demand close monitoring. I bring adult dogs in once a year unless my veterinarian advises more frequent visits because of ongoing health concerns or chronic medications. I schedule checkups for senior dogs every 6 months due to higher risks of age-related diseases or sudden health changes.
Factors That Influence Dog Wellness Exam Frequency
| Factor | Impact on Exam Frequency |
|---|---|
| Chronic Conditions | Increase in visit frequency for disease management |
| Breed Risk | Extra exams for breeds predisposed to certain conditions |
| Environment | More frequent visits for high-risk geographic areas |
| Medical History | Shorter intervals after past health concerns |
Dogs with chronic illnesses like diabetes or heart disease get seen more often for monitoring and medication management. Some breeds—like Boxers or Dachshunds—may need additional checkups for breed-specific risks. I increase visits for dogs living in regions with prevalent parasites or infectious diseases. My veterinarian shortens intervals after hospitalizations or when past medical issues increase ongoing risk.
Every dog benefits from a tailored wellness exam schedule. I rely on my veterinarian to set the best frequency, based on age, health status, breed, and environment, so my dog gets timely preventive care and early intervention when necessary.
What to Expect During Your Dog’s Wellness Exam
During a wellness exam, my veterinarian conducts a thorough review of my dog’s overall health status. I observe a series of standardized steps that prioritize early problem detection and preventive care. Each step focuses on essential health indicators relevant to my dog’s breed, age, and lifestyle.
Physical Examination
A comprehensive physical exam includes inspection and palpation of the eyes, ears, mouth, skin, coat, limbs, and abdomen. My veterinarian uses a stethoscope to listen to heart and lung sounds.
| Physical Exam Area | Examples of Checks | Common Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Eyes | Discharge, cloudiness, redness | Cataracts, infections |
| Ears | Odor, debris, inflammation | Ear infections, mites |
| Mouth | Tartar, gum health, missing/broken teeth | Gingivitis, dental disease |
| Skin and Coat | Bumps, bald patches, parasites | Allergies, fleas, ticks |
| Abdomen | Palpation for pain, abnormal lumps | Tumors, organ enlargement |
| Limbs and Joints | Mobility, swelling | Arthritis, sprains |
| Heart & Lungs | Rhythm, breath quality | Heart disease, respiratory issues |
Vaccination and Parasite Prevention Review
My veterinarian updates my dog’s vaccination status based on lifestyle and regional risk factors. Vaccination schedules are tailored according to prior history and age. Parasite screening involves tests for intestinal parasites, heartworms, fleas, and ticks.
| Vaccine Type | Commonly Given For | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Core Vaccines | Rabies, distemper, parvo | Annually or triennially |
